Cloud Computing: Reimagining How We Build, Scale, and Deliver Technology
Introduction
Cloud computing is no longer just a tech buzzword—it's the backbone of modern digital transformation. From startups to governments, cloud platforms have become critical for scalability, agility, and innovation.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services — including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence — over the internet (“the cloud”). These services are typically provided on-demand and follow a pay-as-you-go pricing model.
Instead of owning and maintaining physical infrastructure, organizations can rent/use computing resources from cloud providers like Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
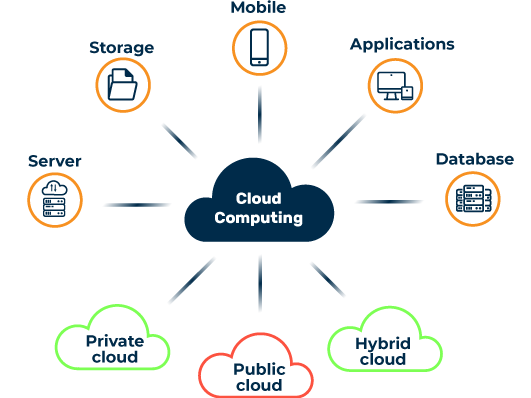
Key Characteristics
2. Broad Network Access: Services are available over the internet and accessible from a variety of devices.
3. Resource Pooling: Cloud providers serve multiple customers using a shared pool of resources.
4. Rapid Elasticity: Resources can scale up or down dynamically to meet demand.
5. Measured Service: Usage is monitored, controlled, and billed based on consumption.
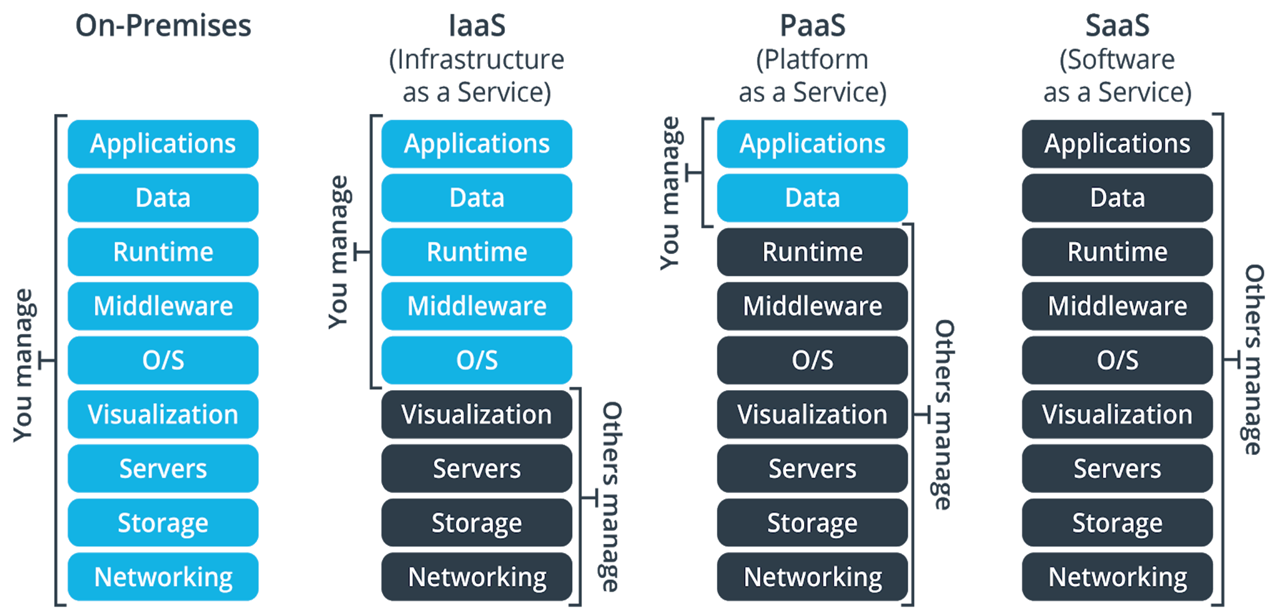
Cloud Service Models
Provides virtualized computing resources (e.g., VMs, storage, networks).
Example: Azure Virtual Machines, Amazon EC2
Offers a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of managing the infrastructure.
Example: Azure App Services, Google App Engine
Delivers applications over the internet, typically on a subscription basis.
Example: Microsoft 365, Salesforce
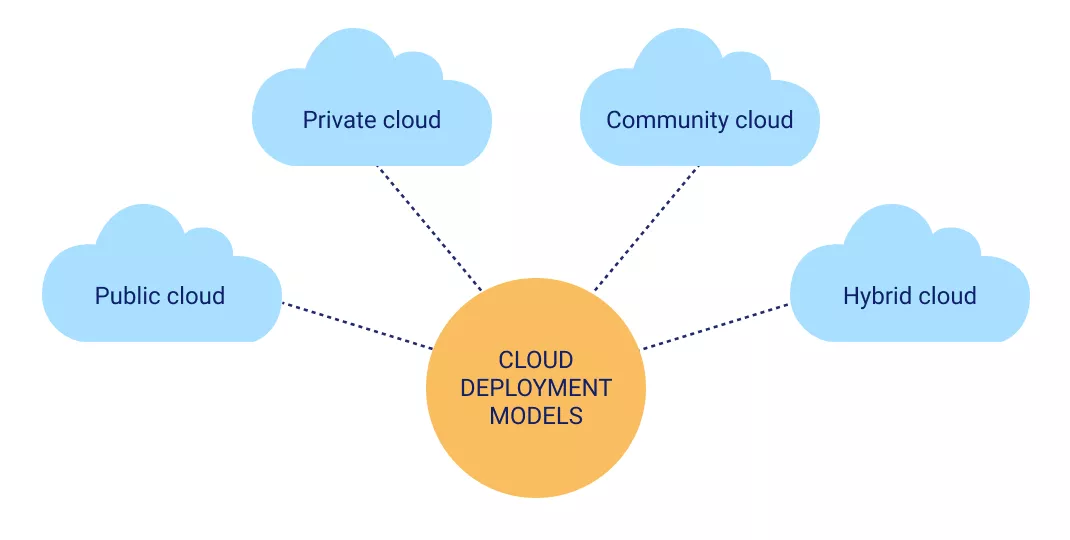
Cloud Deployment Models
Public Cloud: Owned and operated by third-party providers (e.g., Azure, AWS).
-
Private Cloud: Dedicated infrastructure operated for a single organization.
-
Hybrid Cloud: A mix of public and private clouds that allows data and applications to move between them.
-
Multi-Cloud: Using services from multiple cloud providers for flexibility and resilience.
Why Cloud Computing Matters?
Cost Efficiency: Reduces capital expenses on hardware and software.
-
Scalability: Instantly adjusts resources to meet dynamic demand.
-
Security: Major providers offer enterprise-grade security and compliance.
-
Business Continuity: Enables disaster recovery and high availability.
Innovation: Accelerates development through AI, analytics, and DevOps tools.
Final Thoughts
As a Cloud Architect and Tech Lead, understanding and applying cloud principles is essential to building future-ready, secure, and resilient systems.